-
1.India’s oil and gas sector is under mounting pressure from regulators,
investors, and communities to deliver measurable climate action instead of just pledges.2.The sector must reduce emissions, curb methane leaks and flaring, meet ESG norms, adopt circular waste systems, and secure financing for green transitions.
3. Global oil majors like ADNOC and ExxonMobil are investing billions in renewables and carbon capture; India’s ONGC is committing Rs 2 trillion to decarbonisation.
4. Integrated Sustainability Solutions (ISS) offers execution-focused support through brands like ReIgnite, Re Analytical, and netZERO, bridging the gap between planning and on-ground action.
5. The energy transition is inevitable, and companies need to embed
sustainability at every stage and use tools like digital traceability and circular economy practices to lead change.
Over the past decade, sustainability has become a business-critical priority for India’s oil and gas sector. Investors, regulators, and communities are no longer satisfied with corporate pledges; they demand proof, measurable action, and lasting impact. The coming decade will define which companies simply talk about change and which ones are recognised for engineering it. While many leading firms have set ambitious decarbonisation and ESG targets, the biggest gap remains execution.
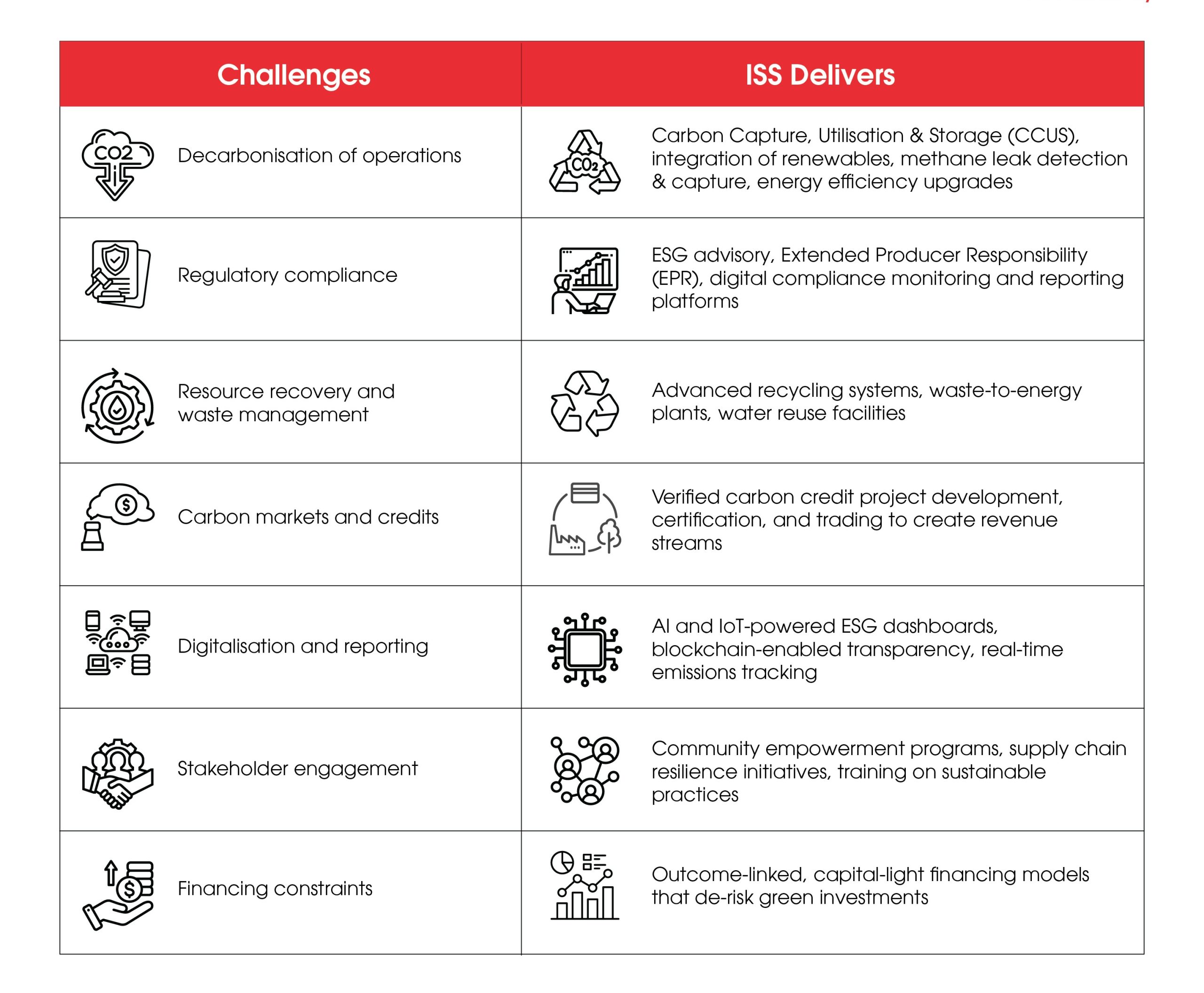
This is where Integrated Sustainability Solutions (ISS) and its brands ReIgnite for decarbonisation, Re Analytical for advanced testing and monitoring, and netZERO for EPR and carbon credits step in. We move beyond advisory to deliver end-to-end implementation, helping oil and gas players bridge the distance between boardroom ambition and on-site transformation.
Globally, leaders in oil and gas are showing that transformation is possible. The
International Energy Agency calls for halving emissions intensity by 2030 and reducing
methane by 75 percent through leak detection, flaring elimination, and electrification.
The IPIECA and WBCSD SDG Roadmap guides the sector on embedding the UN
Sustainable Development Goals into strategy. Abu Dhabi’s ADNOC is investing US $5
billion annually in low-carbon energy and carbon capture to achieve net zero by 2045,
proving that large national oil companies can scale renewables without compromising
growth. ExxonMobil is directing US $30 billion by 2030 into carbon capture, biofuels,
hydrogen, and lithium, illustrating how traditional majors are pivoting towards the
energy transition. These global moves underline a critical truth: the energy transition is not optional, it is inevitable. India, too, has begun charting its course. ONGC has
committed nearly ₹2 trillion (approximately US $24 billion) for decarbonization,
renewable integration, and green hydrogen.
ISS understands the oil and gas industry’s realities: heavy legacy infrastructure, fluctuating energy markets, and mounting stakeholder pressure.
India’s oil and gas sector faces a high-stakes balancing act: ensuring energy security for a fast-growing economy while decarbonising operations to align with global climate imperatives. The key hurdles include reducing operational emissions in energy- intensive facilities, managing methane leaks and flaring, adapting to evolving ESG and compliance frameworks, recovering waste and water through circular systems, unlocking carbon finance and credit revenues, building real-time visibility and digital traceability, and securing financing for large-scale green transitions.

Let's Get
- In Touch
